Bias or systematically favoring certain outcomes. Temur holds an information session to prepare her students for an upcoming project.

Solved Collecting Data Bias And Experimental Design 1 4 Chegg Com
The aim of this paper is to raise the awareness of three specific forms of information bias in observational and experimental medical research study designs.
. Bias in experimental study designs. Psych 203 Chapter 1 Quiz Abnormal Psychology. Occur when participants act differently simply because they know that they are.
In general an adaptive design may be acceptable if the trial is well designed. The most common form of participant bias comes in the form of various types of demand characteristics. By increasing the dilution factor and favoring the number of replicates over the number of.
Providing the control group with a placebo treatment protects against bias caused by expectancy. Three Biases that can impact research. E following situations identify the sampling method used.
This has often been described as the participant reacting purely to what they think the researcher desires but this can also occur for less obvious reasons. In the currently proposed design the potential 18-month delay from the time of completion of enrollment in the Phase II portion of the trial and initiation of. The most common of these will be explained.
This could lead to bias in the estimated intervention effect in this case making the intervention effect look artificially low. Accordingly priming a future orientation could provide a relatively straightforward and inexpensive way to reduce present bias. We present clear and simple strategies to improve the decision-making process.
Off label use of imaging databases could lead to bias in AI algorithms New study highlights the problems that can arise when data published for one task are used to train algorithms for a. Experimenter bias is a human incompetency of being objective and inciting towards subjectivity. These quasi-experiments can potentially lead to what is called selection bias where the effect of the treatment is confounded with pre-existing differences in the treated and control sequence groups.
For each of th. Experimenter bias Experimenters sometimes make errors in recording data that tend to favor the experimental hypothesis. 33 This can lead to increased dropout in the experimental or control arms either of which can affect results.
Which of these experimental designs could lead to bias. A Confounding can lead to bias B confounding can conflict with randomization C Confounding can lead to uncertainty as to which variable is causing an effect D Confounding can make it more difficult to separate subjects into treatment and control groups E Confounding can negate the benefits of blinding. These research findings are relevant for practice in infrastructure and beyond.
On these basic designs. B Phil and Bart race down the street to determine who is the fastest. C A car company pays participants to.
Also if a sample is small then again the researchs outcome would be biased. We distinguished in class and in the notes between biased data that arise from invalid or poor experimental designs and biased evaluation of models. First the primary analysis adjusted for several patient-level factors that could be associated with the outcome or with completing screening before becoming overdue.
In previous semesters she has learned that when students base their project on the brief project outline and they do not ask questions they experience _____ which can lead them to be generally underprepared and underperform overall. We will review the major sources of bias in the section on threats to internal and. This person lives alone in the country but doesnt interfere with others lives.
Even choosing a wrong or an inaccurate way of data analysis could lead to a quantitative bias. Then explain how the sampling method could lead to bias. Experimental designs that study two or more independent variables at the same time are called factorial designs.
There are conflicting recommendations as to the minimum number of observations needed for a time series design but they range from 20 observations before and 20 after intervention implementation to 100 observations overall. Some quasi-experimental designs are immune to certain specific selection biases and it has been widely suggested that this immunity is linked to the absence. Factors may lead to the ultimate effect outcome.
These four criteria provide a rigorous basis for determining the most effective apportionment of total effort among replicates and dilution levels. These are self-reporting bias and the often-marginalized measurement error bias and confirmation bias. The choice of the wrong statistical test or the misuse of tests eg running many comparisons may cause biased results.
Although the generalizability of this work to racial bias in American contexts is uncertain the findings raise important questions in need of investigation domestically. Both of these methods display. Quasi-experimental methods to test for evaluator bias.
These quasi-experiments can potentially lead to what is called selection bias where the effect of the treatment is confounded with pre-existing differences in the treated and control sequence groups. A Two mice are given the choice between Swiss and American cheese. A researcher spends 15 or more hours per day conducting experiments or doing library reading and records observations on color-coded index cards.
A farmer brings a. These findings add to the growing evidence that construal-level interventions can elicit differences in designer decision-making. One of the central biases that can hamper and negatively impact research is that of participant bias.
24 9 The interrupted time series design is the most effective and powerful quasi-experimental design particularly when supplemented by other. How to Avoid Experimenter Bias. Any differences in mood between the experimental and control groups can now be attributed to the drug itself rather than to experimenter bias or participant expectations see figure.
Experimental designs have been developed to reduce biases of all kinds as much as possible. Some quasi- experimental designs are immune to certain specific selec- tion biases and it has been widely suggested that this im-. Several of these studies have estimated gender bias in grading by.
These 3 studies demonstrating. An EIS Environmental Impact Statement must be prepared before. Results of a survey showing that abstracts do not contain much information on effect sizeThe x-axis shows which paper in the study pair had the larger absolute effect size A and B are random names for the papersThe y-axis shows the tendency to think paper A had the larger effect which was calculated as Number of participants thinking A was.
Mark all of the following that are experimental design problems that can lead to bias and do not mark those that involve biased model evaluation. The studys analysis plan addressed this in 2 ways. Bias was severe in small assays and could lead in extremely small designs to overestimation of effector frequency by as much as 100.

Quasi Experimental Study Designs Series Paper 6 Risk Of Bias Assessment Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology

Solved 1 3 Introduction To Experimental Design I And 2 Do Chegg Com

Designing To Avoid Identification Bias Rethinking Clinical Trials

Psychology 3450w Experimental Psychology Ppt Download

Pdf The Use Of Quasi Experimental Designs For Vaccine Evaluation Semantic Scholar

Solved One Reason Why Psychologists May Use Chegg Com
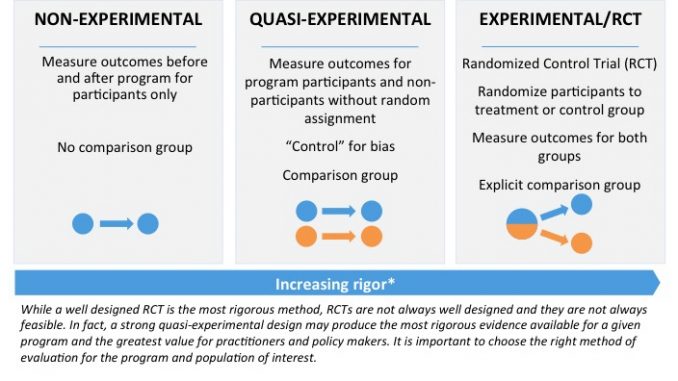
20 Differences Between Randomized Controlled Trial Rct And Quasi Experimental Study Design Public Health Notes
0 comments
Post a Comment